
Features
- High digestibility for optimal nutrient absorption
- Prebiotic fibers like FOS (fructooligosaccharides) and chicory root to support a healthy microbiome for gastrointestinal health
- Rich in EPA and DHA reduce intestinal inflammatory response
- Complete and balanced for long term feeding adult dogs
ST-O-ne GUARD formulated to manage urolithiasis1
Recommended For
- Pancreatitis
- Hyperlipidemia
- Lymphangiectasia
- Protein-losing enteropathy
- Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
- Acute gastrointestinal illness
- Chronic enteropathies
- Other gastrointestinal diseases requiring a low-fat diet
Recommended For
- Growth, pregnancy, or lactation
- PROBLEM
Disease State Education
Compared with proteins and carbohydrates, fats are the most complex nutrient to digest and absorb.1 Complete digestion requires a variety of organ and enzymatic activity, including involvement of the pancreas, liver, gall bladder and lymphatic system.

Because of its complexity, fat digestion is easily compromised and some dogs with gastrointestinal diseases have difficulty digesting fat (see Figure 1). Fat malabsorption can stimulate colonic water secretion and exacerbate diarrhea and fluid loss, increase mucosal permeability, alter motility, lead to secretory diarrhea and cause intestinal inflammation.1, 2, 3
Research shows that fat-restricted diets tend to be better tolerated in a variety of gastrointestinal diseases.4 In acute gastroenteritis, a highly digestible, low-fat diet is recommended to help optimize mucosal recovery and minimize any exacerbation of diarrhea or vomiting.4 Fat reduction is especially important for dogs at risk for, or diagnosed with, pancreatitis. High-fat, low protein foods have been associated with the development of pancreatic and hepatic lipidic changes in dogs, and consumption of high fat foods contributes to obesity in pets, which, like hypertriglyceridemia, is a common risk factor for pancreatitis. In one report, 43% of dogs with acute pancreatitis were considered overweight or obese. A low-fat diet, therefore, is recommended for all obese or hypertriglyceridemic patients with acute or chronic pancreatitis.5
In cases of intestinal lymphangiectasia (IL), characterized by dilation of the intestinal lymphatic vessels, dietary fat restriction has also been shown to be an effective treatment.6 Lymphangiectasia may develop as a primary or congenital condition or be secondary to damage to or increased pressure in these lymphatics from chronic intestinal inflammation and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In either case, protein-rich lymph can leak from the abnormal lymphatic vessels, resulting in protein-losing enteropathy (PLE). Fat restriction helps to decrease lymphatic flow, thereby reducing lymphatic pressure and protein loss.4 Restricting dietary fat can also help reduce the risk of distension and emesis associated with prolonged gastric retention, and is recommended for symptomatic management of borborygmus and flatulence in such cases absent of a primary diagnosis.4 Therefore, highly digestible, fat-restricted diets are advocated as appropriate and important in managing GI disease and diarrhea in many situations.1, 2, 3
Dietary Fat Limitation
Fat malabsorption can stimulate colonic water secretion and exacerbate diarrhea and fluid loss, increase mucosal permeability, alter motility, lead to secretory diarrhea and cause intestinal inflammation.1-3 Research shows that fat-restricted diets tend to be better tolerated in a variety of gastrointestinal diseases.4
Table 1. Average Key Nutrient Analysis Values for BLUE GI Low Fat Dry Formula for Dogs
| Fat | EPA + DHA | |
|---|---|---|
| As-Fed % | 7.60 | 0.16 |
| Dry Matter % | 8.26 | 0.17 |
| g/100 kcal | 2.33 | 0.05 |
| Recommended | For obese and hypertriglyceridemic dogs with pancreatitis, ≤ 10% DM5 For IBD, 8 - 12% DM with fiber enhancement12 |
For IH13 For IBD13 |
Prebiotic Fiber
Prebiotic fibers are fermented in the colon to produce short-chain fatty acids, which play a significant role in promoting healthy enterocyte metabolism.7 Prebiotic fibers also help balance and support a healthy intestinal microbiome, modify intestinal pH and enhance the immune system.8, 9, 10, 11
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Due to their anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3 fatty acids from sources such as fish and flaxseed can have a beneficial effect in controlling mucosal inflammation and aiding in the recovery of the gastrointestinal mucosa. In addition to meeting criteria for fat restriction, BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat food for dogs also contains omega-3 fatty acids, including EPA and DHA (eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acids), to help manage conditions such as pancreatitis, idiopathic hyperlipidemia (IH) and inflammatory bowel disease (see Table 1).
Enhanced Digestive Efficiency
Feeding readily digestible proteins, carbohydrates and fats is important in diets intended to manage gastrointestinal diseases. Greater digestibility is associated with reduced osmotic diarrhea due to fat and carbohydrate malabsorption, reduced intestinal gas and lowered antigenicity of bowel contents as smaller amounts of protein are absorbed intact.12 Adequate energy density and digestibility are also important in low-fat diets, as fat is a diet’s most concentrated source of calories.
- EVIDENCE
BLUE Clinical Data
- EVIDENCE
BLUE Clinical Data
- 1. Determining Digestibility And Energy Density
- 2. Determining Stool Quality
- 3. Urine Relative Supersaturation (RSS) Evaluation
Determining Digestibility And Energy Density
Purpose
Prove that Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Gastrointestinal Low Fat food is easily digestible in healthy dogs.
Study Design
Six (6) clinically healthy, adult dogs, four (4) male and two (2) female, from a commercial research facility were enrolled and placed on BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat dry formula for dogs as their sole source of nutrition for 11 days.
The dogs were housed individually in standard, species-appropriate housing and managed consistently during the study, including providing access to activity/exercise. Each dog was presented with food on an individual basis. Cages and bowls were cleaned daily and sanitized in accordance with the Animal Welfare Act.
The dogs were fed once daily at the same time each day. Body weights were recorded on Days 1 through 6, and on Day 10. The first five (5) days of the test were considered an acclimation period. Food consumption was recorded daily. Days 6 through 11 were fecal collection days. After the final fecal collection, each of six (6) individual fecal samples, as well as a sample of the BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat food, was sent to a commercial laboratory for analytical determination.14
The results of the analyses on the feces and the diet were used to calculate dry matter, protein, and caloric digestibility and metabolizable energy, according to the recommended protocol defined by Method 1 of the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO).15
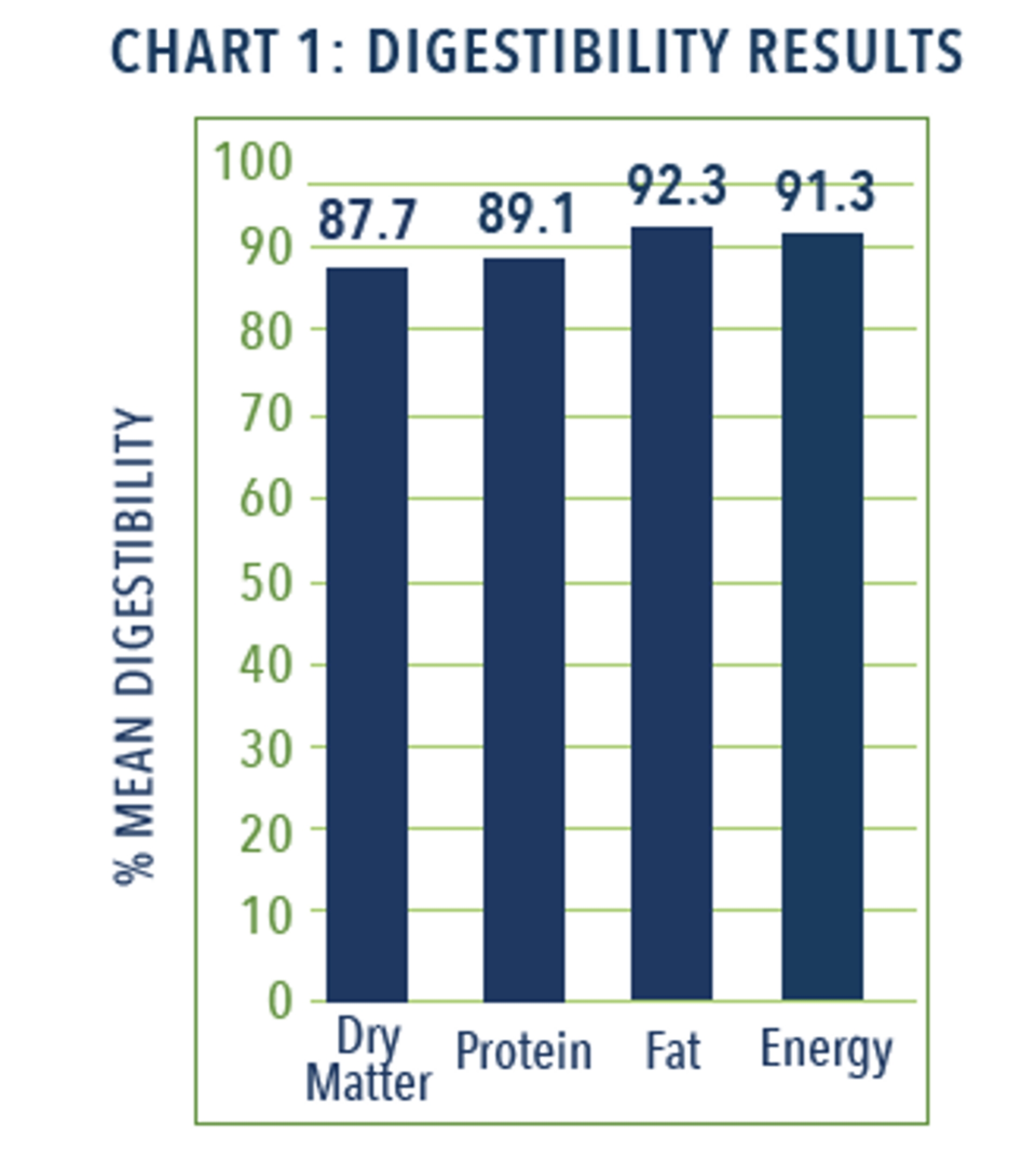
Results12
Study results show that BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat dry formula for dogs is highly digestible (see Chart 1), with a mean calculated metabolizable energy (ME) of 3266 kcals/kg.16
Determining Stool Quality

Purpose
Prove that BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat food for dogs results in ideal stool quality.
Study Design
Two (2) groups of adult dogs (n=10 each for Canine Stool Quality Studies 1 and 2) from a commercial research facility were enrolled in the studies. All animals were clinically healthy. Dogs were individually fed BLUE Natural Veterinary
Diet™ GI Low Fat dry formula once daily as their sole source of nutrition for 7 days.
Stool consistency observations were made a minimum of three (3) times daily during the collection period for each dog, and stools were collected a minimum of three (3) times daily, or as often as needed, during the collection period to ensure a clean sample for each individual dog. Stools were weighed and recorded daily during the collection period for each individual dog. The scoring scale ranged from 1 for diarrhea to 5 for hard, dry crumbly feces and was aided by photographs of examples. In this study, a stool score between 3 and 4 is considered to represent ideal fecal consistency for dogs.
Results
Overall, feeding BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat dry formula for dogs was clinically proven to result in ideal stool consistency. Importantly, most stools were moist, formed (score of 3) or well-formed, sticky (score of 3.5) stools, with a mean score of 3.1816 (see Figure 2).
Urine Relative Supersaturation (RSS) Evaluation
Purpose
To show that feeding BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat food for dogs results in urine relative supersaturation (RSS) values less than 2.5 for struvite or less than 10 for calcium oxalate, which have been shown to limit the formation of these types of uroliths.
Study Design
Ten (10) adult dogs, ages 3 to 8 years old, were enrolled in each of the RSS studies. All dogs selected were clinically healthy and were maintained in standard, species-appropriate housing, managed consistently during the study and provided access to activity/exercise. The study protocols were reviewed and approved by the research facility’s institutional animal care and use committee. Studies were performed using both dry and wet formulas. The dogs were fed a BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat diet for 23 days. An amount of food calculated to maintain body weight was offered each day. On the last day of the study, a 24-hour urine sample was collected. From the sample, urine pH was measured via pH meter, and specific gravity was measured with a refractometer. Two (2) aliquots were frozen and shipped to The University of Tennessee for RSS analysis.17
Results12
Feeding BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat wet formula for dogs resulted in a clinically significant urine RSS value <1 for struvite, indicative of an undersaturated solution in which struvite crystals dissolve and do not spontaneously precipitate and uroliths do not form. Feeding the dry formula resulted in a calcium oxalate RSS value <10, indicating a metastable solution where crystals do not spontaneously precipitate and the risk of urolith formation is reduced.
Clinical Impact
The results discussed in this Blue Buffalo Clinical Report, along with existing literature, provide evidence supporting the clinical efficacy, digestibility, stool quality and palatability for BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat food for dogs. These findings support that BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Low Fat food provides an ideal approach to nutritionally manage dogs with a gastrointestinal condition and difficulty digesting fat, while satisfying pet owners’ preferences for wholesome, natural diets.
Nutritional Information
Animal feeding tests using AAFCO procedures substantiate BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Gastrointestinal Support Low Fat for Dogs provides complete and balanced nutrition for maintenance of adult dogs.
Nutritional Analysis
| Nutrient | As-Fed (Average) |
Dry Matter Basis (Average) |
Per 100 kcals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 25.00% | 27.17% | 7.65 g |
| Crude Fat | 7.60% | 8.26% | 2.33 g |
| Carbohydrate (NFE) | 49.87% | 54.21% | 15.27 g |
| Crude Fiber | 4.00% | 4.35% | 1.22 g |
| Total Dietary Fiber | 10.75% | 11.68% | 3.29 g |
| Insoluble Fiber | 9.14% | 9.93% | 2.80 g |
| Soluble Fiber | 1.61% | 1.75% | 0.49 g |
| Ash | 5.83% | 6.34% | 1.79 g |
| Calcium | 0.80% | 0.87% | 0.24 g |
| Phosphorus | 0.60% | 0.65% | 0.18 g |
| Sodium | 0.40% | 0.43% | 0.12 g |
| Chloride | 0.59% | 0.64% | 0.18 g |
| Potassium | 0.99% | 1.08% | 0.30 g |
| Magnesium | 0.12% | 0.13% | 0.04 g |
| Iron | 188.61 mg/kg | 205.01 mg/kg | 5.77 mg |
| Copper | 15.95 mg/kg | 17.34 mg/kg | 0.49 mg |
| Manganese | 21.19 mg/kg | 23.03 mg/kg | 0.65 mg |
| Zinc | 166.73 mg/kg | 181.23 mg/kg | 5.11 mg |
| Iodine | 3.32 mg/kg | 3.61 mg/kg | 0.10 mg |
| Selenium | 0.58 mg/kg | 0.63 mg/kg | 0.02 mg |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 0.86% | 0.93% | 0.26 g |
| DHA | 0.11% | 0.12% | 0.03 g |
| EPA | 0.05% | 0.05% | 0.02 g |
| Omega-6 Fatty Acids | 1.34% | 1.46% | 0.41 g |
| Linoleic Acid | 1.20% | 1.30% | 0.37 g |
| Arachidonic Acid | 0.06% | 0.07% | 0.02 g |
| Taurine | 0.29% | 0.32% | 0.09 g |
| L-Carnitine | 175.00 mg/kg | 190.22 mg/kg | 5.36 mg |
| Vitamin C | 175.00 mg/kg | 190.22 mg/kg | 5.36 mg |
| Vitamin E | 600.00 IU/kg | 652.17 IU/kg | 18.37 IU |
| Vitamin A | 25554.50 IU/kg | 27776.63 IU/kg | 782.44 IU |
| Vitamin D3 | 1260.14 IU/kg | 1369.72 IU/kg | 38.58 IU |
| Glucosamine | 336.05 mg/kg | 365.27 mg/kg | 10.29 mg |
| Chondroitin | 506.40 mg/kg | 550.43 mg/kg | 15.51 mg |
Metabolizable Energy
| kcal/cup | 297 |
| Grams/cup | 91 |
| kcal/kg (ME Calculated) | 3,266 |
| % ME from Protein | 27 |
| % ME from Fat | 20/td> |
| % ME from Carbohydrates | 53 |
Recommended Daily Feeding Chart
| Up to 15 lbs. | ½ - 1 ½ cups* |
| 16 to 25 lbs. | 1 ½ - 2 ¼ cups* |
| 26 to 40 lbs. | 2 ¼ - 3 ¼ cups* |
| 41 to 60 lbs. | 3 ¼ - 4 ½ cups* |
| 61 to 80 lbs. | 4 ½ - 5 ½ cups* |
| 81 to 100 lbs. | 5 ½ - 6 ½ cups* |
| Over 100 lbs. | Feed 6 ½ cups* plus ½ cup for each additional 20 lbs. |
*Use standard 8-oz. measuring cup.
Ingredients
Deboned Whitefish, Chicken Meal, Pea Protein, Potatoes, Tapioca Starch, Pea Starch, Peas, Natural Flavor, Potato Starch, Plain Dried Beet Pulp, Flaxseed (source of Omega-3 Fatty Acids), Pea Fiber, Canola Oil (source of Omega-6 Fatty Acids), Apple Pomace, Calcium Carbonate, Salt, Cranberries, Pumpkin, Dehydrated Alfalfa Meal, Potassium Citrate, DL-Methionine, L-Threonine, Choline Chloride, Alfalfa Nutrient Concentrate, Dried Kelp, Hydrolyzed Yeast, Fructooligosaccharides, Citric Acid, Taurine, Vitamin E Supplement, L-Tryptophan, Sweet Potatoes, Carrots, preserved with Mixed Tocopherols, Zinc Amino Acid Chelate, Iron Amino Acid Chelate, L-Ascorbyl-2-Polyphosphate (source of Vitamin C), L-Carnitine, Dicalcium Phosphate, Vegetable Juice for color, Blueberries, Barley Grass, Parsley, Turmeric, Dried Kelp, Yucca Schidigera Extract, Copper Amino Acid Chelate, Manganese Amino Acid Chelate, Niacin (Vitamin B3), Calcium Pantothenate (Vitamin B5), L-Lysine, Biotin (Vitamin B7), Vitamin A Supplement, Dried Yeast, Zinc Sulfate, Dried Enterococcus faecium fermentation product, Dried Lactobacillus acidophilus fermentation product, Dried Aspergillus niger fermentation extract, Dried Trichoderma longibrachiatum fermentation extract, Ferrous Sulfate, Dried Bacillus subtilis fermentation extract, Thiamine Mononitrate (Vitamin B1), Riboflavin (Vitamin B2), Vitamin D3 Supplement, Vitamin B12 Supplement, Pyridoxine Hydrochloride (Vitamin B6), Calcium Iodate, Copper Sulfate, Folic Acid (Vitamin B9), Manganese Sulfate, Sodium Selenite, Oil of Rosemary.

BLUE Natural Veterinary Diet™ GI Gastrointestinal Support Low Fat for Dogs is formulated to meet the nutritional levels established by the AAFCO Dog Food Nutrient Profiles for adult maintenance.
Nutritional Analysis
| Nutrient | As-Fed (Average) |
Dry Matter Basis (Average) |
Per 100 kcals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 10.56% | 43.82% | 12.53 g |
| Crude Fat | 2.59% | 10.75% | 3.07 g |
| Carbohydrate (NFE) | 7.30% | 30.29% | 8.66 g |
| Crude Fiber | 0.52% | 2.16% | 0.62 g |
| Total Dietary Fiber | 0.94% | 3.90% | 1.12 g |
| Insoluble Fiber | 0.69% | 2.86% | 0.82 g |
| Soluble Fiber | 0.25% | 1.04% | 0.30 g |
| Ash | 2.54% | 10.54% | 3.01 g |
| Calcium | 0.47% | 1.95% | 0.56 g |
| Phosphorus | 0.34% | 1.41% | 0.40 g |
| Sodium | 0.16% | 0.66% | 0.19 g |
| Chloride | 0.34% | 1.41% | 0.40 g |
| Potassium | 0.36% | 1.49% | 0.43 g |
| Magnesium | 0.03% | 0.12% | 0.04 g |
| Iron | 49.09 mg/kg | 203.69 mg/kg | 5.82 mg |
| Copper | 6.36 mg/kg | 26.39 mg/kg | 0.75 mg |
| Manganese | 5.23 mg/kg | 21.70 mg/kg | 0.62 mg |
| Zinc | 45.90 mg/kg | 190.46 mg/kg | 5.44 mg |
| Iodine | 0.59 mg/kg | 2.45 mg/kg | 0.07 mg |
| Selenium | 0.21 mg/kg | 0.87 mg/kg | 0.02 mg |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 0.23% | 0.95% | 0.27 g |
| DHA | 0.06% | 0.25% | 0.07 g |
| EPA | 0.03% | 0.12% | 0.04 g |
| Omega-6 Fatty Acids | 0.43% | 1.78% | 0.51 g |
| Linoleic Acid | 0.36% | 1.49% | 0.43 g |
| Arachidonic Acid | 0.05% | 0.20% | 0.06 g |
| Taurine | 0.16% | 0.66% | 0.19 g |
| L-Carnitine | 59.92 mg/kg | 248.63 mg/kg | 7.11 mg |
| Vitamin C | 76.90 mg/kg | 319.09 mg/kg | 9.12 mg |
| Vitamin E | 185.90 IU/kg | 771.37 IU/kg | 22.05 IU |
| Vitamin A | 31444.00 IU/kg | 130474.11 IU/kg | 3730.04 IU |
| Vitamin D3 | 473.20 IU/kg | 1963.49 IU/kg | 56.13 IU |
| Glucosamine | 59.93 mg/kg | 248.67 mg/kg | 7.11 mg |
| Chondroitin | 213.19 mg/kg | 884.61 mg/kg | 25.29 mg |
Metabolizable Energy
| kcal/12.5 oz. can | 299 |
| Grams/12.5 oz. can | 354 |
| kcal/kg (ME Calculated) | 843 |
| % ME from Protein | 44 |
| % ME from Fat | 26 |
| % ME from Carbohydrates | 30 |
Recommended Daily Feeding Chart
| Adult up to 30 lbs. | Feed ¾ - 1 ¼ can per 10 lbs. of body weight per day |
| Adult over 30 lbs. | Feed ⅔ - 1 can per 10 lbs. of body weight per day |
Refrigerate unused portion.
Ingredients
Whitefish, Potatoes, Chicken Broth, Water, Chicken Liver, Chicken, Pea Flour, Dried Egg Product, Pea Protein, Pea Fiber, Natural Flavor, Pumpkin, Flaxseed, Calcium Sulfate, Apples, Guar Gum, Salt, Potassium Chloride, Dried Chicory Root, Cassia Gum, Carrageenan, Taurine, Cranberries, L-Tryptophan, Choline Chloride, Turmeric, L-Threonine, DL-Methionine, Vitamin E Supplement, L-Ascorbyl-2- Polyphosphate (source of Vitamin C), L-Carnitine, Thiamine Mononitrate (Vitamin B1), Zinc Amino Acid Chelate, Iron Amino Acid Chelate, Copper Amino Acid Chelate, Manganese Amino Acid Chelate, Sodium Selenite, Cobalt Amino Acid Chelate, Niacin Supplement (Vitamin B3), Calcium Pantothenate (Vitamin B5), Vitamin A Supplement, Riboflavin Supplement (Vitamin B2), Biotin (Vitamin B7), Vitamin B12 Supplement, Potassium Iodide, Pyridoxine Hydrochloride (Vitamin B6), Vitamin D3 Supplement, Folic Acid (Vitamin B9).

References
- Marks SL. Advances in dietary management of gi disorders. World Small Animal Veterinary Association World Congress Proceedings, 2013.
- Guilford WG. Nutritional management of gastrointestinal diseases. In: Guilford WG, Center SA, Strombeck DR, et al, eds. Strombeck’s Small Animal Gastroenterology, 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders Co, 1996a; 889-910.
- Laflamme DP, Xu H, Long GM. Effect of diets differing in fat content on chronic diarrhea in cats. J Veterinary Int Med 2011 Mar; 25(2):230-235.
- Cave N. Nutritional management of gastrointestinal diseases. Applied Veterinary Clinical Nutrition 1st Edition. Wiley-Blackwell, 2012; 175-220.
- Davenport DJ, Remillard RL, Simpson K. Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis In: Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition. Topeka, KS: Mark Morris Associates, 2010; 1143-1153.
- Okanishi H, Yoshioka R, Kagawa Y, Watari T. The clinical efficacy of dietary fat restriction in treatment of dogs with intestinal lymphangiectasia. J Vet Intern Med 2014;28:809-817.
- Koruda M, Rolandelli R, Settle R, et al. The effect of short chain fatty acids on the small bowel mucosa. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990;51:685–690.
- Sparkes AH, Papasouliotis K, Sunvold G, Werrett G, et al. Effect of dietary supplementation with fructooligosaccharides on fecal flora of healthy cats. Am J Vet Res.1998 Apr;59(4):436-40. © 2023 Blue Buffalo Company, Ltd. CR-10
- Willard MD, Simpson RB, Cohen ND, Clancy JS. Effects of dietary fructooligosaccharide on selected bacterial populations in feces of dogs. Am J Vet Res 2000;61: 820–825.
- Terada A, Hara H, Oishi T, Matsui S, et al. Effect of Dietary Lactosucrose on Faecal Flora and Faecal Metabolites of Dogs. Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease, 2011, Vol. 5: 87-92.
- Field CJ, McBurney MI, Massimino S, Hayek MG, Sunvold GD. The fermentable fiber content of the diet alters the function and composition of canine gut associated lymphoid tissue. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1999 Dec 30;72(3-4):325-41.
- Davenport DJ, Jergens AE, Remillard RL. Inflammatory Bowel Disease In: Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition. Topeka, KS: Mark Morris Associates, 2010; 1065-1076.
- Bauer J. Therapeutic use of fish oils in companion animals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2011 Dec 1;239(11): 1441-51.
- Eurofins USA laboratories, Des Moines, Iowa, 2018.
- AAFCO Official Publication of the Association of American Feed Control Officials Inc., Champaign, IL.
- Blue Buffalo Co., Ltd., data on file, 2018.
- University of Tennessee Pharmacology Lab, College of Veterinary Medicine.










